median nerve compression test vs tinels|carpal tunnel conduction test : distribute Purpose [edit | edit source]. Tinel's test is used to test for compression . webInteractive Chart for Diageo plc (DEO), analyze all the data with a huge range of indicators.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da O futebol 4raBet é considerado uma excelente plataforma, pois oferece numerosas opções de apostas e odds mais convenientemente. A cada dia você pode apostar em mais .
Step 1. Patient position in standing or sitting. Step 2. The patient forearm is supinated and then the examiner applies direct pressure over the carpal tunnel (median nerve) between the thenar and hypothenar eminence for 30 seconds. Step 3. A positive test indicates any numbness, .
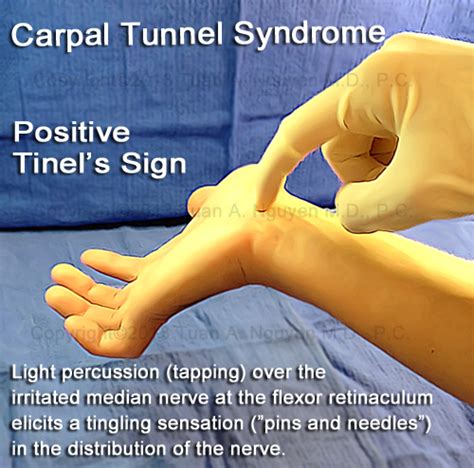
Purpose [edit | edit source]. Tinel's test is used to test for compression .Tinel’s Test: Examiner repeatedly taps over the volar carpal ligament for up to 60 seconds. The test is considered positive if patient reports tingling or electric shocks in distribution of the . A positive Tinel test is defined as pain and/or paresthesia of the median-innervated fingers that occurs with percussion over the median nerve. A positive Tinel sign .A failure to discriminate two points held 5 mm or less apart from one another, in the median nerve innervated digits, is a positive test suggestive of CTS: 4.5: Positive Tinel sign
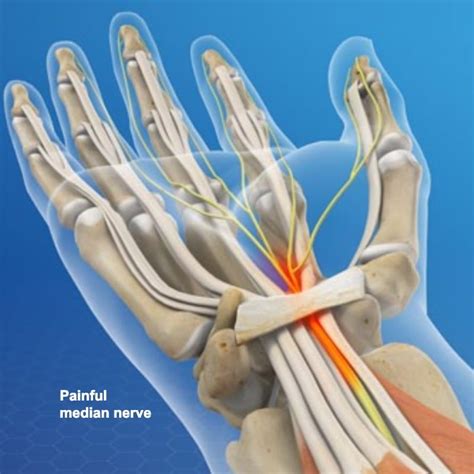
The median nerve compression test is also called Durkan’s test. Mostly commonly, compression of the median nerve results in carpal tunnel syndrome. Pathophysiology. Compression neuropathy arises when there is more than .median nerve, which branches off proximal to the carpal tunnel. Therefore, decreased sensation over the thenar eminence indicates a median nerve lesion proximal to the carpal tunnel.
Carpal Compression Test (Apply pressure with thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, located just distal to the wrist crease. The test is positive if the patient responds with numbness and tingling within 30 . Tinel’s test: positive if tapping lightly over the median nerve at the wrist produces paraesthesia or pain in the median nerve distribution. Carpal tunnel compression test (Durkan’s test) : is positive if pressure over the .
Key Points. Carpal tunnel syndrome is compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Symptoms include pain and paresthesias in the median nerve .
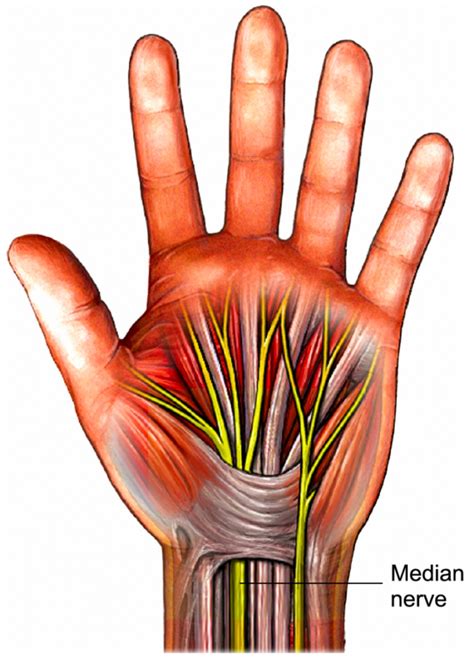
The median nerve innervates the muscles of the thenar compartments of the palm, flexor pollicis longus, abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis, and adductor pollicis. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common acquired compressive neuropathy of the median nerve that presents with symptoms of numbness and tingling in the median nerve distribution of the hand. . Tinel’s sign, previously known as the Hoffman-Tinel sign, is something doctors use to check for nerve problems. It’s commonly used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome.
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Pronator Teres Syndrome (PTS) is a compression neuropathy of the median nerve at the elbow. It is not as common as compression at the wrist which is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS). PTS . Tinel’s sign (lightly tapping over the nerve to see if it generates a tingling sensation) Phalen’s test (pushing the dorsal surface of hands together and holding 30 – 60 seconds) Carpal Compression Test (Apply pressure with thumbs over the median nerve within the carpal tunnel, located just distal to the wrist crease. The test is positive .Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis of carpal compression test (CCT), Tinel’s test (TT) and Phalen’s test (PT) for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) . Chen JP, Hsu YW, Yeh CK. Assessment of median nerve mobility by ultrasound dynamic imaging for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0147051 . The Tinel sign test dates back to 1915 and is used to check for nerve problems called neuropathies. Experts disagree about how well the test works. . a condition caused by compression in the .
Pronator Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the median nerve at the level of the elbow. . and positive Tinel's over the proximal volar forearm. Treatment involves a prolonged nonoperative course, and rarely, surgical decompression. . may exclude other sites of nerve compression or identify double-crush syndrome. Differential. AIN . Other specialized tests to be considered on the physical exams for carpal tunnel syndrome include the Phalen maneuver, Tinel sign, and median nerve compression test. The Phalen maneuver is when a patient flexes their wrist 90 degrees with their elbows in full extension. Recreation of symptoms of the carpal tunnel within 60 seconds is a positive .Tinel's test — positive if tapping lightly over the median nerve at the volar surface of the wrist produces paraesthesia or pain in the median nerve distribution. Durkan's test (carpal tunnel compression test) — positive if direct pressure over the proximal edge of the transverse carpal ligament (proximal wrist crease) with the thumbs . The Tinel test involves firm percussion performed over the course of the median nerve just proximal to or on top of the carpal tunnel. A positive Tinel test is defined as pain and/or paresthesia of the median-innervated fingers that occurs with percussion over the median nerve. . With increased compression of the median nerve, focal .
Nerve compression syndromes of the hand present with various signs and symptoms that correspond to the nerve involved and its anatomic distribution. There are three nerves and their corresponding branches that provide sensory and motor innervation to the hand that include the median, ulnar, and radial. An understanding of the anatomy and distribution of .the Tinel sign. 10. To perform the hand eleva-tion test, the patient raises his or her hands . Median nerve compression test 64 83 Apply direct pressure over the transverse carpal ligament .
The median nerve is one of the main nerves in the hand. It originates as a group of nerve roots in the neck; these roots then come together to form a single nerve in the arm. The median nerve travels down the upper arm, across the elbow, and into the forearm, then passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist on its way to the hand and fingers. Patients were assessed using a symptom questionnaire, Phalen's test, Hoffmann-Tinel's sign, hand elevation test, carpal compression test, tourniquet test, pressure aesthesiometry and two-point .The six clinical tests included Tinel’s sign, wrist flexion with fingers extended, wrist flexion with fingers flexed, wrist extension, combined wrist extension/median nerve pressure and combined wrist flexion/median nerve pressure. . McMurtry RY. Median nerve compression test in carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis. Reproduces signs and .Cubital tunnel syndrome (CBTS) is a peripheral nerve compression syndrome. It is an irritation or injury of the ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel at the elbow. This is also termed ulnar nerve entrapment and is the second most .
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a mononeuropathy caused by compression of the posterior tibial nerve or its branches in the foot/ankle [1]. TTS is analogous to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, but occurs much more rarely, and usually as a .
tinel sign carpal tunnel syndrome
Tinel’s test. Tinel’s test is used to identify median nerve compression and can be useful in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. To perform the test, simply tap over the carpal tunnel with your finger. Interpretation. If the patient develops tingling in the thumb and . Pronator and anterior interosseous nerve syndromes are the two most common compression neuropathies of the median nerve occurring around the elbow. 22 Pronator syndrome occurs with compression of .
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, and is the 2nd most common compression neuropathy of the upper extremity. It typically presents with paresthesias of the small and ring finger, and can be treated with both nonoperative modalities such as elbow splinting. If these fail and symptoms are severe surgical ulnar nerve . Notes. Variations exist between studies on the location and number of taps necessary to elicit a positive response, and in some studies the test is performed by tapping the median nerve in 20 degrees of wrist extension, while others tap along the path of the median nerve up to where the median nerve enters the carpal tunnel.. The Tinel sign is elicitable . The median nerve is usually damaged at either the elbow, due to a fracture of the humerus bone of the upper arm, or the wrist, due to either carpal tunnel syndrome or a wrist laceration or gashing. If the median nerve is damaged at the elbow region, it is known as a proximal injury to the median nerve.
synovial noninflammatory fibrosis and thickening leads to median nerve compression (most common) compression leads to microvascular insufficiency causing ischemic damage to the nerve. Presentation. . Tinel test. percussion over the course of the median nerve. pain and/or paresthesia in the median nerve distribution is a positive test. .
Pronator teres syndrome (PTS), first described by Henrik Seyffarth in 1951, is caused by a compression of the median nerve (MN) by the pronator teres (PT) muscle in the forearm. [1][2] The PT muscle is named because of its action and shape; it is a rounded muscle that pronates the forearm. In the majority of cases (66%), it arises from unequal two heads: the .Tinel’s sign is one of the best known and widely used clinical diagnostic tools in hand surgery, plastic surgery, neurology, and orthopedics. 6 Sensory radial nerve compression symptoms may be confused with the symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis owing to pain with ulnar deviation of the wrist, and in some cases, both conditions may be present simultaneously. 3 Overall, Tinel’s test is a simple yet effective way to help diagnose nerve compression or irritation in the wrist and guide further evaluation and treatment. . The pinch grip test, also known as the pinch grip strength test, assesses median nerve compression or dysfunction, especially in carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). What. The Hoffman-Tinel sign, now more commonly known as the Tinel sign, was defined in 1915 by Paul Hoffmann and Jules Tinel as the "pins and needle feeling" elicited by tapping on a nerve proximally, with resulting paresthesia experienced in the corresponding distal cutaneous distribution of an injured peripheral nerve. Hoffmann and Tinel both individually .

lg g4 drop test with case
WEB13 de set. de 2023 · As apostas em grupo no bolão da Quina custam desde R$ 12,50, mas a cota mínima é de R$ 3,50 por participante. A Caixa permite de duas a 50 cotas nessa modalidade. Ninguém acertou os números .
median nerve compression test vs tinels|carpal tunnel conduction test